Is internal energy a state function?
Yes, internal energy is a state function.
Internal energy is the total energy of a system, including the kinetic energy of the particles and the potential energy of the intermolecular forces.
A function whose value depends entirely on the state (temperature, pressure etc.), independent of the path by which the function reached that state, is called a state function.
Suppose, a closed system moves from state A to state B in path-I and returns from state B to state A in path-II.
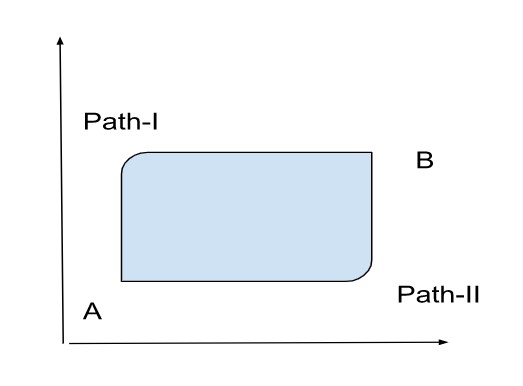
The internal energy of the system at state A is UA and the internal energy of the system at state B is UB. then
Change in internal energy of system along path-I = UB – UA
Change in internal energy of system along path-II = UA – UB
If the change in internal energy along path-I is greater than the change in internal energy along path-II, then some energy will be generated as the closed system moves from state A to state B and from state B back to state A. As a result, if this process happens again and again, energy will be produced continuously. But this is strictly against the 1st law of thermodynamics.
So change in internal energy in path-I = change in internal energy in path-II, i.e.
UB – UA = UA – UB
Therefore, when a system changes from one state to another, the change in its internal energy depends only on the initial and final states and never on the path.
So if this system moves from state A to state B in two or more paths, there will be an equal amount of internal energy change. i.e.
ΔU= UB – UA = UA – UB
A cycle is completed by the system moving from state A to state B along path-I and returning from state B to state A along path-II, so integration of U = 0. So it can be said that the magnitude of U depends only on state and not on path i.e. it is path neutral. Therefore internal energy is a state function or state dependent thermodynamic entity.